Jaundice is apparent, nevertheless determining its cause requires a physician’s examination, blood assessments, and sometimes different other tests.
Warning signs
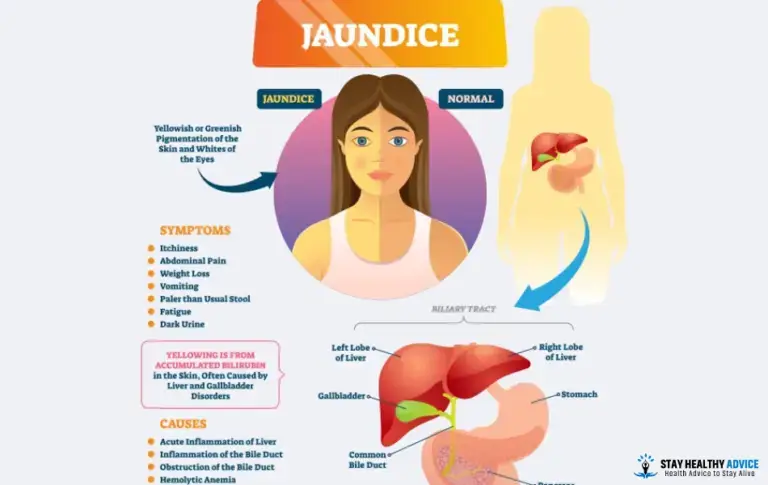
In individuals with jaundice, complying with indicators is a factor for the problem:
- Severe stomach pain and inflammation
- Changes in emotional function, such as sleepiness, disappointment, or confusion
- Blood in faeces or tarry black faeces
- Blood in vomit
- Fever
- A tendency to bruise or to haemorrhage quickly, often leading to a red-purple outbreak of tiny dots or bigger smudges (which suggest blood loss in the skin)
When to See a Physician
If people have any type of indication, they should see a physician ASAP. Individuals without indicators must see a doctor within several days.
What the Doctor Does
Medical professionals originally ask about issues concerning the individual’s symptoms, signs and case history. Doctors after that do a health examination. What they discover throughout the background and health examination generally suggests a reason and the tests that might be required to be done (see Table Some Causes and Characteristics of Jaundice).
They additionally ask when pee starts to look dark (which normally occurs before jaundice is established). People are asked about various other indications, such as irritability, exhaustion, alterations in stool, and tummy pain. Medical professionals are especially thinking of symptoms and signs that are a significant factor. For instance, abrupt anorexia nervosa, queasiness, vomiting, discomfort in the abdomen, and fever recommend liver illness, especially in young people and people with dangerous aspects of liver disease.
Heat and extreme, continuous pain in the upper ideal part of the abdominal locations advise intense cholangitis (infection of the bile air ducts), usually in individuals with a clog in a bile duct. Serious cholangitis is considered a professional emergency.
Medical professionals ask individuals whether they have had liver problems, whether they have had surgical treatment that included the bile air ducts, and whether they take any medications that can create jaundice (as an example, the prescription medicines amoxicillin/clavulanate, chlorpromazine, azathioprine, and contraceptive pills; alcohol; non-prescription medicines; medical herbs; and other natural items such as teas). Understanding whether relatives have really in addition had jaundice or different other liver disorders can help medical professionals recognize genetic liver problems.
Considering that hepatitis is a common factor, doctors ask especially worrying problems that boost the danger of liver disease, such as.
- Running at a preschool.
- Staying in or operating at an institution with long-term property owners, such as a psychological healthcare facility, prison, or lasting treatment facility.
- Living in or taking a trip to a location where hepatitis prevails
- Taking part in anal sex
- Consuming raw shellfish
- Infusing illegal or leisure drugs
- Having hemodialysis
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes
- Acquiring a tattoo or body piercing
- Operating in a medical care facility without being immunized against liver conditions
- Having had a blood transfusion before 1992
- Making love with a person who has liver disease
- Having been born between 1945 and 1965
Throughout the physical examination, doctors search for signs of serious problems (such as high temperature, truly minimized high blood pressure and a quick heart rate) and for indicators that liver function is significantly damaged (such as very easy discolouration, an outbreak of little dots or smudges, or modifications in mental function). They delicately press on the stomach area to try to find swellings, tenderness, swelling, and other irregularities, such as a bigger liver or spleen.
Physicians will certainly probably start with the individual’s background and a physical examination to detect jaundice. They may later likewise acquire laboratory tests.
During an evaluation, they will certainly take notice of the abdomen, liver, and skin.
The medical professional might frequently include lab evaluations to help identify the underlying source of jaundice. These consist of:
- Bilirubin examinations: A high degree of unconjugated bilirubin compared to levels of conjugated bilirubin suggest hemolytic jaundice.
- Full blood count (FBC) or complete blood count (CBC): This figures out levels of red blood cells, leukocytes, and platelets.
- Liver condition A, B, and C examinations: This assessment for a range of liver infections.
The doctor will certainly furthermore assess the structure of the liver if they believe an obstruction. In these circumstances, they will use imaging evaluations, including MRI, CT, and ultrasound scans.
On top of that, they might do an endoscopic backwards cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). This is a procedure incorporating endoscopy and X-ray imaging.
The AAFP specifies that a healthcare expert might perform a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy can look for swelling, cirrhosis, cancer cells, and fatty liver. This examination involves inserting a needle right into the liver to obtain a cell sample. A healthcare specialist will certainly analyze the example through a tiny lens.